Salesforce has consistently focused on simplifying processes through its emphasis on point-and-click tools, and AgentForce is a continuation of that mission. With tools like Agent Builder, Model Builder and Prompt Builder, businesses can quickly build and launch AI agents without needing deep technical skills.
This makes AI more accessible, allowing companies to use advanced AI features to improve their processes.
Introducing Agentforce
Agentforce is Salesforce’s innovative platform, allowing businesses to create, deploy and manage AI agents tailored to their needs. These agents go beyond traditional chatbots, offering proactive, autonomous capabilities to handle tasks like lead qualification, customer support, and order management.
Built on Salesforce’s powerful platform, Agentforce integrates smoothly with Customer 360, allowing businesses to utilize their existing data, workflows and tools.
Core Features of Agentforce
- Reasoning Engine: At the heart of Agentforce is its advanced reasoning engine, which helps agents understand context, take action and make decisions. It combines structured data, like customer information and policies, with real-time inputs to adapt dynamically to various business situations.
- Data Integration: AI’s success depends on the quality and relevance of the data it can access. With Salesforce’s Data Cloud, Agentforce can connect structured and unstructured data, giving agents the context to provide accurate responses and take practical actions.
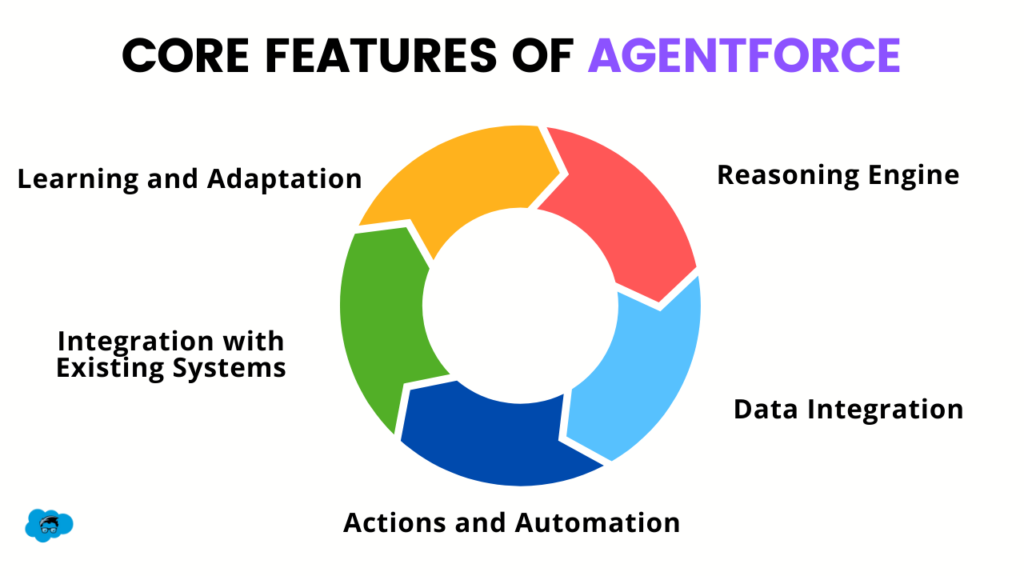
- Actions and Automation: Agents built on Agentforce can perform various tasks, from updating records and sending notifications to executing complex workflows. Businesses can easily define and adjust agent behaviour without extensive programming using Salesforce tools like Flows, Apex, and Prompt Templates.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Agentforce easily integrates with your existing Salesforce applications and external systems through APIs and data connectors, facilitating smooth workflows across platforms. This removes compatibility concerns and enables your team to concentrate on essential tasks without disruptions.
- Learning and Adaptation: Agentforce’s AI agents continuously learn from interactions, refining their algorithms to improve accuracy and effectiveness. This development transforms them into virtual employees who become smarter with each engagement, enhancing decision-making and providing evolving support tailored to your organization’s needs.
Also Read: Salesforce Winter’25 Release Flow Features and Updates
Building an Agent: Key Elements
When setting up an agent with Salesforce’s Agentforce, there are five key things you need to decide. These parts guide what the agent does, how it acts and what limits it has, ensuring it works well for your business.
Here’s an overview of each:
Role
The role outlines what the agent is designed to do, from handling customer queries to managing leads or offering sales advice. Defining the role gives the agent a clear purpose, guiding actions and responses to align with your business needs.
Examples
- A Sales Agent might focus on following up with leads and crafting personalized responses to potential customers.
- A Customer Service Agent could assist with troubleshooting, answering common questions or escalating issues when needed.

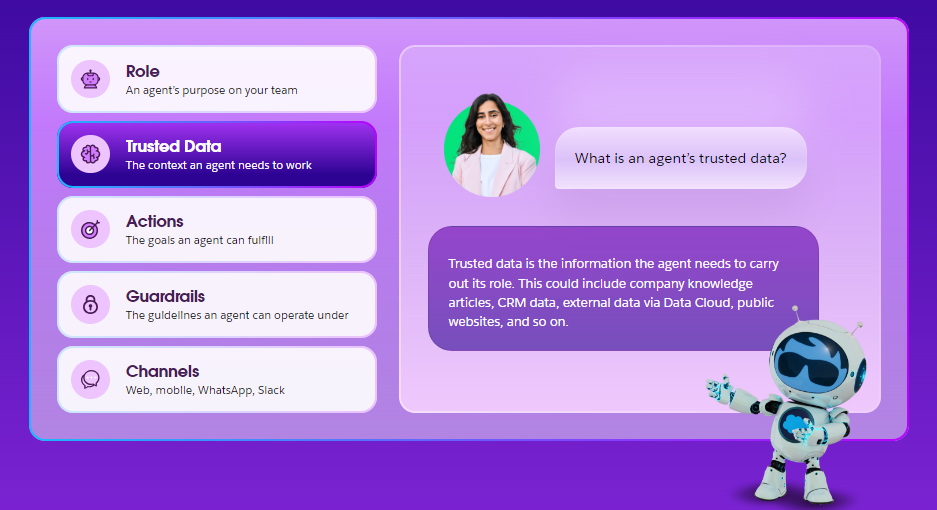
 Data
Data
The “Data” aspect determines what information the agent can access, including structured data like CRM records and unstructured data like emails or chat transcripts.
Broader data access makes the agent more competent. For example, a Sales Agent with access to CRM and previous email interactions can respond more accurately to customer needs.
- Structured Data: Includes customer records, product catalogues or sales data. The agent uses this to find information, make decisions and respond appropriately.
- Unstructured Data: Refers to email threads, call transcripts or social media messages. This data helps the agent better understand the context and respond more personalized.
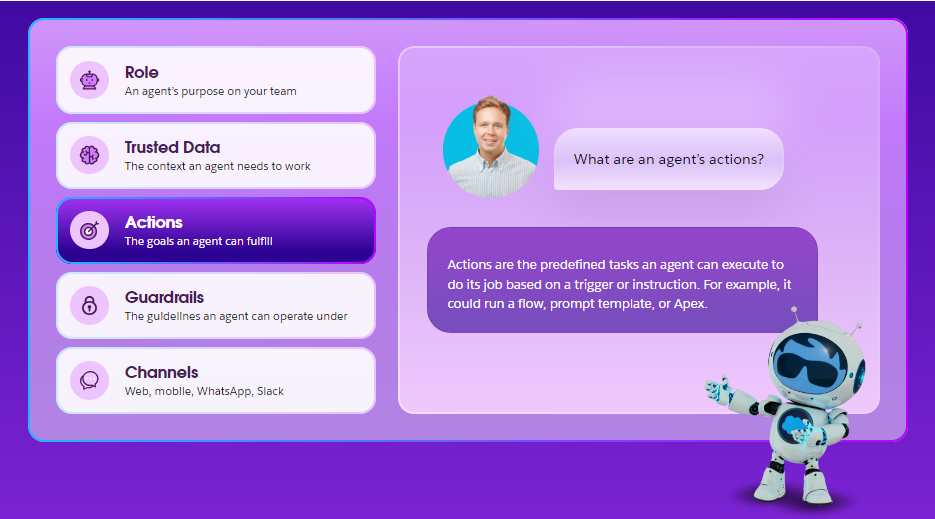
Actions
The Actions element defines what the agent is allowed to do. This goes beyond answering questions—it includes executing business processes using tools like Salesforce Flows, APIs, or custom code.
It is where the agent truly adds value by taking on previously manual tasks, allowing your team to focus on more complex work.
Examples
- Updating Salesforce records.
- Sending emails or notifications.
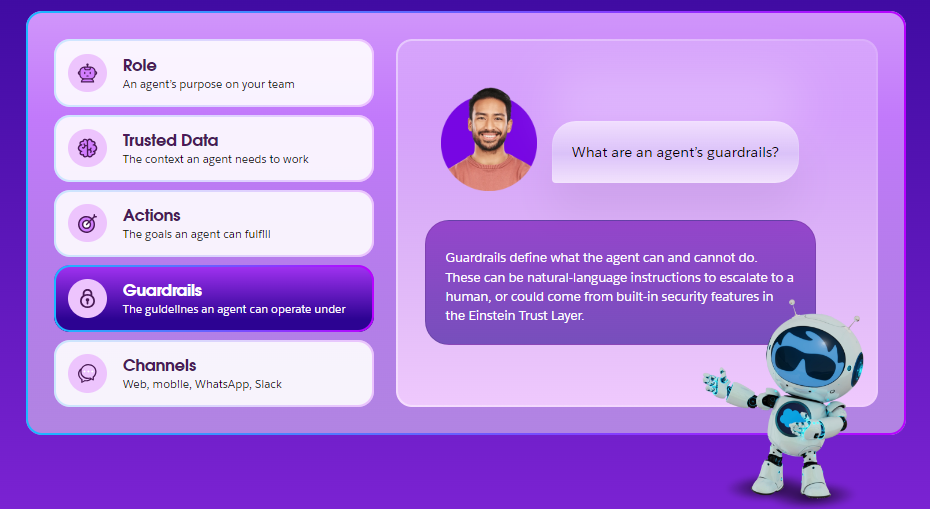
Guardrails
Guardrails set limits on what the agent can and can’t do. These rules ensure that the agent operates within ethical and legal boundaries, protecting your business from risks like data breaches or unauthorized actions.
- Einstein Trust Layer: Provides privacy features such as data masking and prompt injection defence, ensuring the agent uses data responsibly.
- Ethical Guardrails: These help filter out inappropriate or harmful content.
- Business Guardrails: Include role permissions and data access rules, limiting the agent to authorized actions only.
Channel
The Channel is where the agent communicates through SMS, WhatsApp, Slack, or even voice. The platform depends on how you want the agent to interact with users, whether customers or employees.
Examples
- An agent on SMS or WhatsApp can provide quick, real-time responses to customer queries.
- Voice agents can handle phone calls, guiding users through processes.
Launch Plans and What Lies Ahead
Agentforce will be available to everyone starting October 25, 2024, with parts of the Atlas Reasoning Engine launching in February 2025. This gradual rollout gives businesses time to prepare and determine how to integrate this new technology into their operations. It allows companies to plan, ensuring they’re ready to make the most of these tools when they’re fully available.
Want to Learn Salesforce Flows? Checkout our Salesforce Flow Course
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Chatbots, Copilots, and Agents?
Chatbots, Copilots, and Agents each have distinct roles.
- Copilots work alongside employees, assisting them interactively by carrying out tasks as if they were the employees.
- Conversely, Agents are more flexible—they can operate independently, run tasks in the background without human involvement, or work interactively when needed.
- Chatbots generally handle user inquiries and simple automated tasks but don’t offer the more profound task execution that Copilots and Agents provide.
2. What is Agentforce Service Agent?
Agentforce Service Agent is an advanced customer service solution that operates 24/7 using generative AI. Unlike traditional chatbots, it handles tasks, makes decisions, and provides natural responses based on your trusted business data. This allows it to meet customer service goals efficiently while your team focuses on more strategic work.
To learn more, build your first agent with Agentforce.
3. What are the different types of Agentforce Agents?
- Service Agent: Automates 24/7 customer support across channels.
- Einstein Copilot: Assists employees with day-to-day tasks.
- SDR Agent: Qualifies leads and books meetings for sales teams.
- Sales Coach: Provides AI-powered training for sales reps.
Conclusion
In short, Agentforce makes AI more accessible for businesses, allowing anyone to create and manage intelligent agents without technical expertise. Companies can automate tasks and improve customer interactions with user-friendly tools and smooth integration.
As Agentforce becomes available, businesses can begin planning how to incorporate it into their operations to enhance efficiency.







