In this blog, we will explore how we do Number to Word Conversion Using Apex by breaking down the logic step by step. Below is the Apex class, which we have built to contain this logic. So this apex class can be utilised as a helper where we want to use this logic like in a trigger or some flow, based on the requirements.
//Converts numeric values to their English word equivalents (e.g. 1234 -> "one thousand, two hundred thirty four").
public with sharing class NumberToWord {
/** Words for 0–19 (irregulars: eleven, twelve, thirteen, etc.) */
private static final String[] TO_19 = new String[]{
'zero', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'four', 'five', 'six',
'seven', 'eight', 'nine', 'ten', 'eleven', 'twelve', 'thirteen',
'fourteen', 'fifteen', 'sixteen', 'seventeen', 'eighteen', 'nineteen'
};
/** Tens prefix: twenty, thirty, ... ninety. Index i -> 20 + 10*i */
private static final String[] TENS = new String[]{
'twenty', 'thirty', 'forty', 'fifty', 'sixty', 'seventy', 'eighty', 'ninety'
};
/** Thousands-scale names: "", "thousand", "million", "billion", ... Index i -> 1000^i */
private static final String[] DENOM = new String[]{
'', 'thousand', 'million', 'billion', 'trillion', 'quadrillion',
'quintillion', 'sextillion', 'septillion', 'octillion', 'nonillion',
'decillion', 'undecillion', 'duodecillion', 'tredecillion', 'quattuordecillion',
'sexdecillion', 'septendecillion', 'octodecillion', 'novemdecillion', 'vigintillion'
};
// static value for 20
private static final Integer BOUND_19 = 20;
// static value for 100
private static final Integer BOUND_100 = 100;
// static value for 1000
private static final Integer BOUND_1000 = 1000;
//Converts a number 0–99 to English (e.g. 42 -> "forty two").
public static String convert_nn(Integer val) {
return convertUnder100(val);
}
//Converts a number 0–999 to English (e.g. 456 -> "four hundred fifty six").
public static String convert_nnn(Integer val) {
return convertUnder1000(val);
}
//converts any number to English (e.g. 12345 -> "twelve thousand, three hundred forty five").
public static String english_number(Long val) {
if (val == null) {
return 'zero';
}
if (val < 0) {
return 'negative ' + english_number(-val);
}
return englishNumberNonNegative(val);
}
/**
* Overload for Integer. Same as english_number(Long); routes automatically based on value.
*/
public static String english_number(Integer val) {
System.debug('Integer called');
return english_number(val == null ? 0L : (Long)val);
}
/**
* Overload for Decimal (e.g. Currency, Number fields).
*/
public static String english_number(Decimal val) {
if (val == null) {
return 'zero';
}
return english_number(val.longValue());
}
private static String convertUnder100(Integer val) {
if (val == null || val < 0 || val > BOUND_100) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException('convertUnder100 expects 0 <= val <= 100');
}
if (val < BOUND_19) {
return TO_19[val];
}
if (val == BOUND_100) {
return 'one hundred';
}
for (Integer v = 0; v < TENS.size(); v++) {
Integer dval = 20 + 10 * v;
if (dval + 10 > val) {
Integer units = Math.mod(val, 10);
return units != 0 ? TENS[v] + ' ' + TO_19[units] : TENS[v];
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException('convertUnder100 unexpected value: ' + val);
}
private static String convertUnder1000(Integer val) {
if (val == null || val < 0 || val >= BOUND_1000) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException('convertUnder1000 expects 0 <= val < 1000');
}
if (val == 0) {
return 'zero';
}
Integer hundreds = val / BOUND_100;
Integer remainder = Math.mod(val, BOUND_100);
String word = '';
if (hundreds > 0) {
word = TO_19[hundreds] + ' hundred';
if (remainder > 0) {
word += ' ';
}
}
if (remainder > 0) {
word += convertUnder100(remainder);
}
return word;
}
private static String englishNumberNonNegative(Long val) {
// Automatically route by range: 0–99 -> convert_nn, 100–999 -> convert_nnn, 1000+ -> recursive
if (val < BOUND_100) {
return convertUnder100(val.intValue());
}
if (val < BOUND_1000) {
return convertUnder1000(val.intValue());
}
for (Integer v = 0; v < DENOM.size(); v++) {
Integer didx = v - 1;
Integer dval = (Integer) Math.pow(BOUND_1000, v);
if (dval > val) {
Integer mod = (Integer) Math.pow(BOUND_1000, didx);
Integer chunk = (Integer) (val / mod);
Long rest = val - (chunk * mod);
String ret = convertUnder1000(chunk) + ' ' + DENOM[didx];
if (rest > 0) {
ret += ', ' + englishNumberNonNegative(rest);
}
return ret;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException('Value too large for denomination list: ' + val);
}
}
Now lets understand this apex step by step by taking an example. Suppose I have a field on the Quote object where the user will enter the amount in numbers, and there will be another field that holds this amount in words.
Hence, to save users’ time, we will perform number-to-word conversion in Apex.
Step 1: First, we will have a trigger before insert or before update trigger. This trigger will be responsible for initiating the conversion process.
Below is the trigger we have created, which calls a handler class to perform the number-to-word logic.
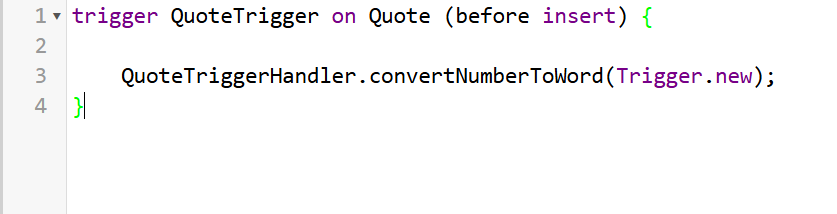
Step 2: Next, the handler class is invoked from the trigger. This handler holds the Quote record details and acts as a centralised place for business logic.
From here, we apply our Number-to-Word Conversion Using Apex logic by calling the helper utility method.
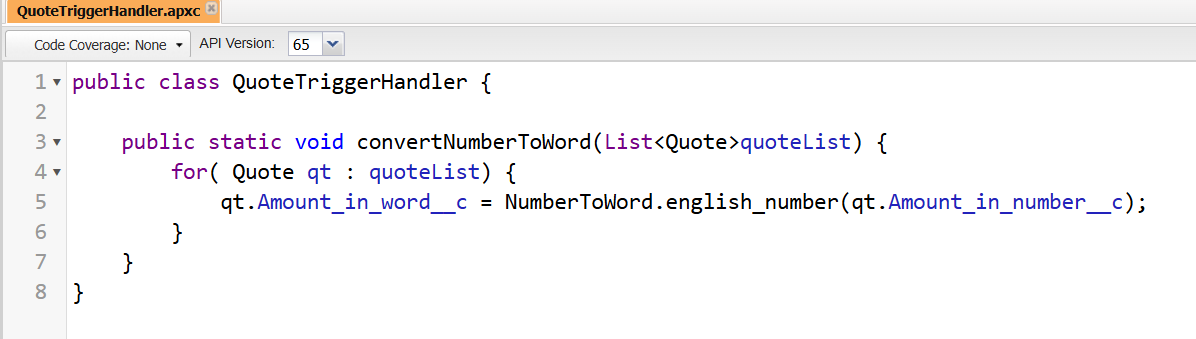
Step 3: As shown above, we have already created two fields to demonstrate how we can utilise this logic. However, these fields can be easily modified or extended based on business requirements.
Now, let’s move on to our main Number-to-Word conversion using Apex Logic. From our TriggerHandler, we have called our method english_number, which will be the main entry point for this logic.
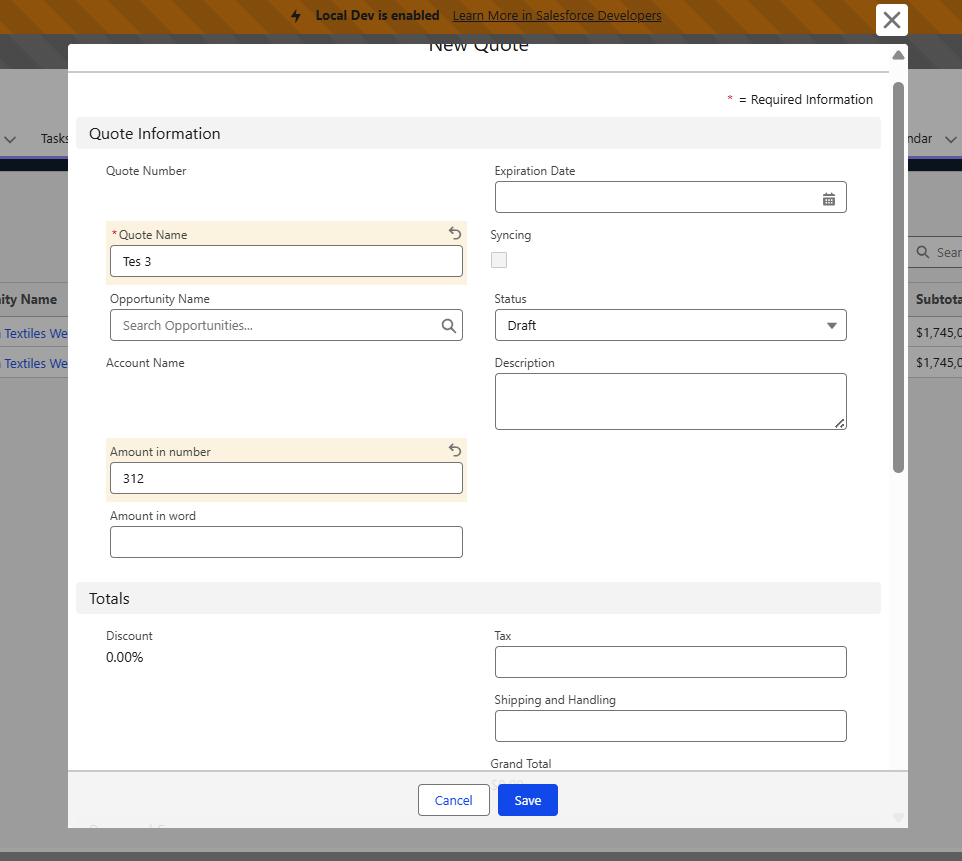
Suppose the user enters 312 in the UI. So english_number method is already overloaded; what type of input we are giving determines which method will get selected.
So, here, english_number(Decimal val) will be called. Subsequently, the value is typecast and routed to the english_number(Long val), which will further call the conversion logic.
Step 4: At this stage, EnglishNumberNonNegative will get executed, and then it will identify the range of our input value. Referring to our input 312, it will then go to the convertUnder1000 method.
Step 5: After moving to convertUnder1000. It will then check a few conditions for the null or negative values. Then it is basically calculating the remainder and the hundreds place.
So at a hundred, we will get the 3, and the remainder we will get the 12. Then to find the word, we are using the TO_19 Array, so for three,e we will get the three, and to process the remainder value into words, we are checking if it is less than 100 or greater than.
Step 6: Finally, we are calling convertUnder100 to process the remainder value. Here we are checking if the value is less than the BOUND_19; if yes, we are checking it in the TO_19 Array. Here, it will find the 12, which will give us the “twelve”. As a result final output becomes three hundred twelve.
OUTPUT

Also Read – Salesforce Apex Best Practices with Real-Time Examples
FAQs
1. Does Salesforce provide a built-in number-to-word conversion feature?
No, we don’t have any built-in method to perform conversion in Salesforce.
2. Does this support currency symbols?
Right now, this only handles number-to-word conversion. But it can easily be extended to support currency formats as needed.
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored Number to Word Conversion Using Apex by breaking down the logic step by step—from trigger execution to handler implementation and finally into a reusable helper class. Basically, this solution will convert numberic value into an English word. This can be a reusable class with minimal enhancement; it can be used for Triggers, Flows, and LWC. Also, other enhancements can be added to this logic, like supporting currency. Since Salesforce does not provide a native way to convert numbers into words, implementing a custom Apex utility becomes essential for meeting real-world business requirements.
Get a complete Roadmap to Learn Salesforce Admin and Development👇







